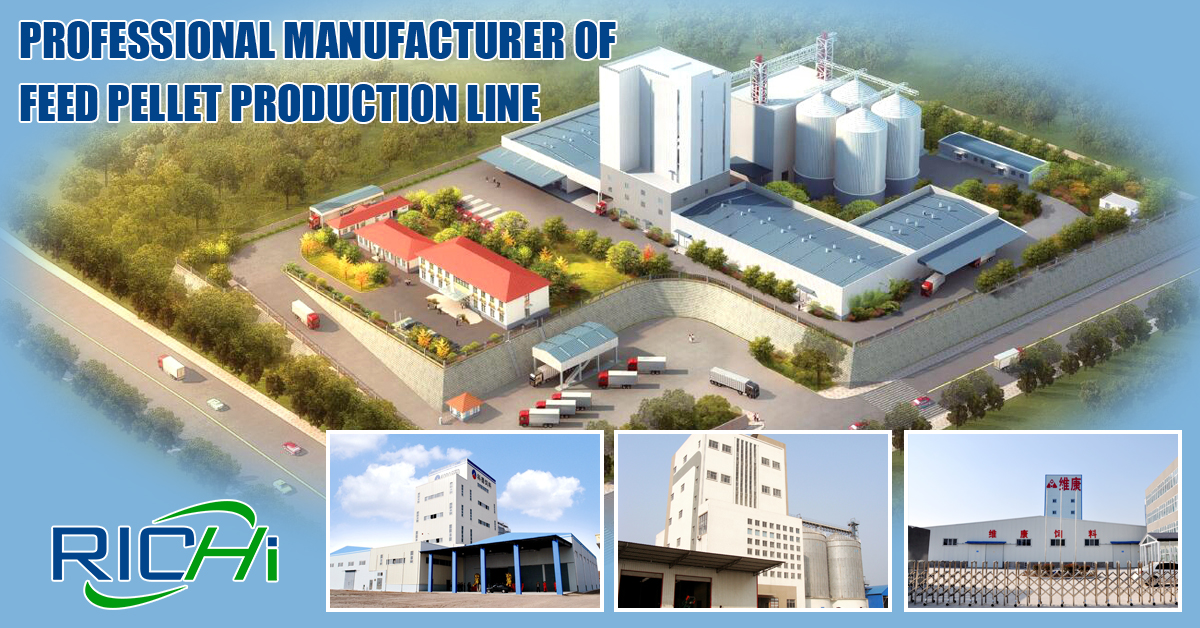
Introduction
An animal feed mill factory is a specialized facility designed to process raw ingredients into nutritionally balanced feed for livestock, poultry, and aquaculture. These plants are essential components of modern agriculture, ensuring that animals receive consistent and high-quality nutrition that promotes growth, health, and productivity.
The demand for Animal Feed Mill Plants has risen globally due to the expansion of intensive animal farming, rising meat and dairy consumption, and the need for efficient feed production systems. Understanding the operational structure, technology, and cost factors is crucial for farmers, feed producers, and investors.
History and Development
The development of animal feed mill plants can be traced back to the early 20th century when mechanized agriculture began replacing traditional feeding practices. Initially, livestock were fed with loose grains or mash, which often led to selective feeding and uneven nutrient intake.
With technological advancements, modern feed mill plants emerged, capable of producing pelleted, crumbled, or mash feed with consistent nutritional content. Innovations in motor technology, die design, and automation have enabled these plants to handle diverse raw materials efficiently. Manufacturers such as RICHI have contributed to modernizing feed production with scalable and durable equipment.
Core Components of an Animal Feed Mill Plant
A typical Animal Feed Mill Plant consists of several key sections:
Raw Material Storage and Handling
Silos, hoppers, and conveyors store and transport raw ingredients
Proper material handling ensures continuous production and minimizes contamination
Grinding and Pulverizing
Hammer mills or roller mills reduce particle size for uniform mixing
Essential for achieving optimal feed digestibility
Mixing and Conditioning
Mixers combine grains, protein meals, vitamins, and additives
Conditioners add moisture and heat to improve pellet quality
Pelletizing or Extrusion
Feed passes through a pellet mill or extruder to form pellets or crumbles
Flat die and ring die pellet mills are common, with suppliers like RICHI providing high-efficiency models
Cooling and Screening
Cooled pellets reduce moisture content, harden for storage, and prevent mold
Screens remove fines and ensure uniform size
Packaging and Storage
Automatic bagging systems facilitate distribution
Allows bulk or bagged feed for commercial or farm use
Types of Animal Feed Mill Plants
Small-Scale Plants
Capacity: 1–5 tons per hour
Suitable for local farms or cooperative feed production
Lower investment, minimal automation
Medium-Scale Plants
Capacity: 5–20 tons per hour
Semi-automated with integrated grinding, mixing, and pelletizing
Ideal for regional feed producers
Industrial-Scale Plants
Capacity: 20–50+ tons per hour
Fully automated, integrated systems
High investment but capable of continuous operation
Modular and scalable designs from manufacturers like RICHI enable easy expansion https://richipelletizer.com/animal-feed-processing-plant/
Raw Materials and Formulation
Animal feed mill plants can process a wide range of raw ingredients:
Cereal grains: corn, wheat, barley, sorghum
Protein meals: soybean meal, cottonseed meal, fish meal
Fibrous materials: rice bran, wheat bran, alfalfa meal
Additives: vitamins, minerals, amino acids, probiotics
Raw material selection affects pellet quality, feed efficiency, and overall plant productivity. The ability to handle diverse ingredients allows feed mills to utilize locally available resources and reduce production costs.
Factors Affecting Animal Feed Mill Plant Price
The Animal Feed Mill Plant price is influenced by multiple factors:
Production Capacity
Higher capacity plants require larger motors, reinforced structures, and precision components
Automation Level
Fully automated feeding, monitoring, and packaging systems increase initial cost but reduce labor and operational errors
Build Quality and Material Selection
Alloy steel dies, rollers, and robust frames improve durability and lifespan
Plant Layout and Infrastructure
Efficient material flow, facility design, and logistics integration affect total investment
Regional Market Factors
Import duties, shipping, and local labor costs influence the final price
Operating Costs and Maintenance
Beyond the initial plant price, operators must consider ongoing costs:
Electricity and energy consumption
Labor expenses
Routine maintenance and replacement of dies, rollers, and bearings
Handling and storage of raw materials
Proper maintenance ensures consistent feed quality, reduces downtime, and prolongs equipment life. Manufacturers such as RICHI Pellet Mill provide technical support to optimize plant operations and maintenance schedules.
Applications in Animal Farming
Animal feed mill plants are used across multiple sectors:
Livestock farms: cattle, sheep, goats
Poultry farms: broilers, layers, breeders
Aquaculture: fish and shrimp farms
Commercial feed mills: supplying bulk feed to regional or national markets
Pelletized feed improves nutrient absorption, reduces wastage, and supports higher productivity and profitability.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
Modern feed mill plants incorporate environmentally friendly practices:
Use of agricultural by-products reduces waste and supports circular economy practices
Energy-efficient motors and systems lower electricity consumption
Pelletized feed improves feed conversion ratios, reducing overall resource use
Dust control and emission systems comply with environmental standards
Sustainable practices contribute to long-term economic and environmental benefits for animal farming operations. Read Full Report
Global Market Trends
Rapid expansion of livestock and poultry industries drives demand for feed mill plants in Asia, Africa, and Latin America
Advances in automation, digital monitoring, and energy efficiency improve production consistency and profitability
Competition among global manufacturers, including RICHI, enhances quality and keeps prices accessible
Modular plant designs allow scalability for emerging markets and small-to-medium enterprises
Conclusion
An Animal Feed Mill Plant is a critical investment for modern livestock, poultry, and aquaculture operations. Factors affecting price include production capacity, automation level, material quality, plant layout, and regional market conditions. Evaluating long-term operational efficiency, maintenance needs, and sustainability ensures that feed producers achieve maximum productivity and profitability from their investment. Pellet machine price in philippines